Introduction: The Digestive Dilemma of GERD and Acid Reflux
As someone who has personally experienced the discomfort and complications of digestive disorders, I understand the importance of differentiating between various conditions to ensure proper treatment and management. In this article, we will delve into the differences between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and acid reflux, two common digestive disorders that are often confused with one another. By understanding the distinctions between these conditions, we can better identify the appropriate treatments and lifestyle adjustments necessary to manage our symptoms and improve our overall digestive health.
Defining GERD: A Chronic Condition of the Esophagus
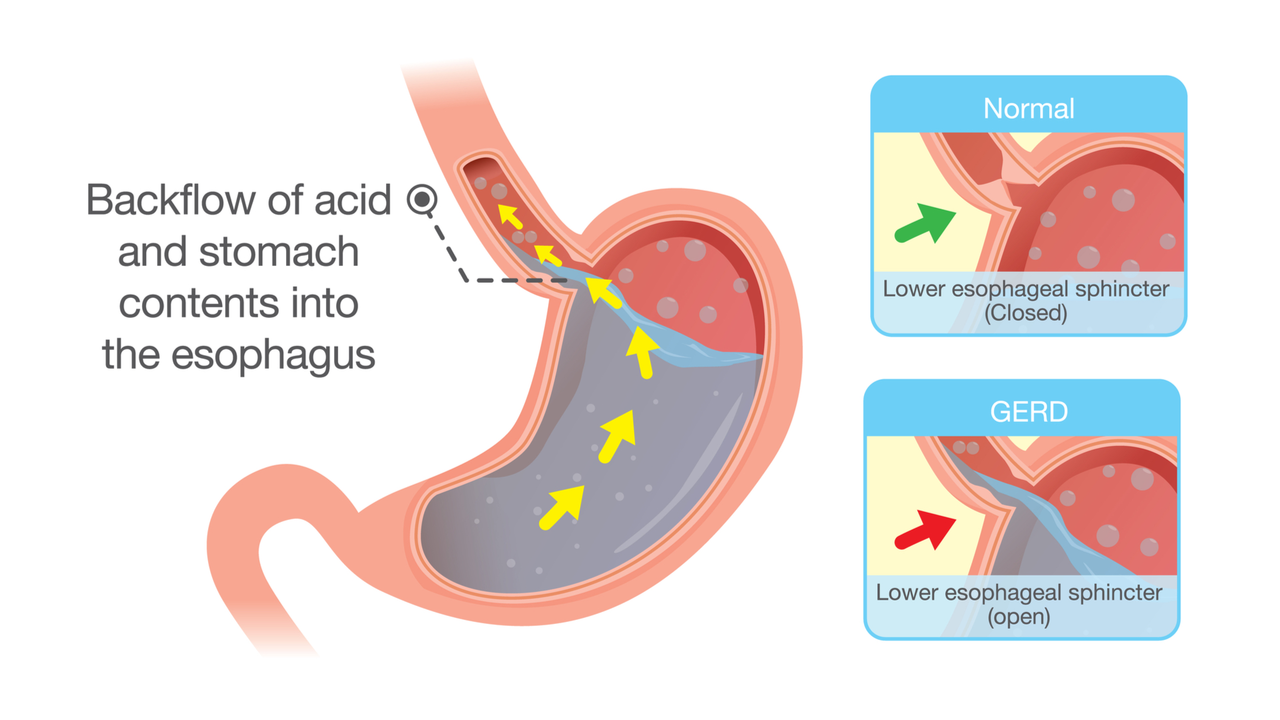
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a chronic condition that affects the esophagus, the tube connecting our mouth and stomach. GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation of its lining. This backflow of acid, known as acid reflux, can lead to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
It is essential to understand that GERD is a chronic and progressive condition. If left untreated, it can lead to complications such as esophageal ulcers, strictures, or even a precancerous condition known as Barrett's esophagus. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize and manage GERD symptoms to prevent long-term damage to the esophagus and maintain a good quality of life.
Unraveling Acid Reflux: A Common and Occasional Occurrence
Acid reflux, on the other hand, simply refers to the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus. It is a common occurrence that most people experience occasionally, often after consuming a large or heavy meal. Acid reflux can cause temporary discomfort, such as heartburn, but it typically does not pose any long-term health risks when experienced infrequently.
It is important to note that while acid reflux is a symptom of GERD, not everyone who experiences acid reflux has GERD. Occasional acid reflux can be managed by making simple lifestyle changes, such as adjusting one's diet or eating habits. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional if acid reflux becomes frequent or severe, as this may be an indication of GERD or another underlying digestive disorder.
Comparing Symptoms: How GERD and Acid Reflux Manifest Differently
Although GERD and acid reflux share some common symptoms, such as heartburn and regurgitation, there are key differences that can help distinguish between these conditions. GERD typically presents with more severe and chronic symptoms, while acid reflux is generally milder and more occasional. Additionally, GERD can cause other symptoms not typically associated with acid reflux, such as chronic cough, hoarseness, and chest pain.
By recognizing the differences in symptom severity and frequency between GERD and acid reflux, we can better determine the most appropriate course of action to manage our digestive health. If we are experiencing chronic or severe symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Identifying Triggers: The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in GERD and Acid Reflux
Both GERD and acid reflux can be influenced by our diet and lifestyle choices. Common triggers for these conditions include consuming large or fatty meals, lying down soon after eating, and certain foods and beverages such as spicy foods, citrus fruits, chocolate, alcohol, and caffeine. Additionally, factors such as obesity, smoking, and certain medications can contribute to the development or exacerbation of GERD and acid reflux symptoms.
By identifying and addressing our individual triggers, we can make positive lifestyle changes to manage our symptoms and improve our digestive health. This may involve making dietary adjustments, losing weight, quitting smoking, or modifying our eating habits, such as eating smaller meals or avoiding lying down soon after eating.
Seeking Treatment: Options for Managing GERD and Acid Reflux
While there are similarities in the management of GERD and acid reflux, the treatment approach for each condition may differ based on the severity and frequency of symptoms. For occasional acid reflux, over-the-counter antacids or acid reducers may be sufficient to provide relief. However, those with GERD often require more aggressive treatment, such as prescription medications, to reduce stomach acid production and promote healing of the esophagus.
In some cases, more advanced treatment options may be necessary to manage GERD, such as endoscopic procedures or surgery. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for our individual needs and ensure the best possible outcome for our digestive health.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between GERD and acid reflux is crucial in managing our digestive health and ensuring that we receive the appropriate treatment and care for our specific condition. By recognizing the distinctions between these disorders and making positive lifestyle changes, we can take control of our digestive health and live a more comfortable, symptom-free life.
Comments (6)
-
Suman Wagle June 12, 2023
Ah, the eternal dance between GERD and casual acid reflux-like comparing a marathon to a sprint you tripped over while reaching for a donut. One could say the chronic sufferer is just the over‑achiever of heartburn, while the occasional spasm is the lazy weekend warrior. Yet, with a pinch of optimism, even the most relentless reflux can learn to keep its fire in check, provided we don’t let it write the script of our dinner plans. So, cheers to learning the rules of this digestive game-and maybe laying off the extra‑spicy taco for once.
-
Neil Sheppeck June 12, 2023
Reading your take feels a bit like watching a philosophical stand‑up routine at a dinner party-entertaining, a dash daring, and oddly comforting. While Suman paints GERD as the marathon runner of heartburn, we might remember that even marathoners need proper training, hydration, and occasionally a light‑hearted jab at their own stubbornness. In practice, those “rules” you mention-like watching portion sizes and steering clear of late‑night tacos-are solid, yet they’re not gospel; they’re more like friendly suggestions from a well‑meaning gym coach. So let’s raise a metaphorical glass to the notion that awareness, not panic, should steer our digestive choices, and maybe we can all agree that the occasional “spicy surprise” doesn’t have to be a capital offense.
-
Stephanie S June 13, 2023
Indeed, the metaphorical gym‑coach analogy works wonderfully, because, as we all know, the digestive system, much like a seasoned athlete, thrives on balanced routines, consistent hydration, and-let’s not forget-mindful pacing; however, when we indulge in the thrill of a midnight burrito, the esophagus may feel, shall we say, like an over‑enthusiastic runner who suddenly sprints uphill without warming up, leading to a cascade of uncomfortable sensations, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and that lingering, echoing cough that refuses to be ignored; therefore, integrating simple practices-like elevating the head of the bed, avoiding tight clothing, and perhaps sipping ginger tea-can act as gentle stretches, preventing the dreaded flare‑ups that often accompany our culinary adventures.
-
Bradley Fenton June 13, 2023
Occasional heartburn is like a fireworks show that never gets invited.
-
Wayne Corlis June 13, 2023
Ah, the fleeting fireworks of occasional heartburn-they sparkle briefly, only to vanish before anyone can truly admire their pyrotechnic charm, and yet we, as chronic sufferers, often find ourselves perpetually standing in the dark, expecting a show that never arrives. This paradox, dear Bradley, is a testament to the whims of our gastrointestinal orchestra, where the occasional flare acts like a rogue trumpet solo in an otherwise muted symphony of quiet digestion. One might argue that the universe, in its infinite benevolence, decided to gift us with this intermittent reminder, just to keep us humble in the face of our own gastronomic ambitions. However, the reality is far less poetic, for each unexpected burn is a signal that the delicate balance between stomach acid and esophageal protection has been momentarily tipped, a reminder that even the most disciplined lifestyle can be upended by a stray peppercorn or an ill‑timed espresso. We must therefore confront this reality with a blend of philosophical resignation and sarcastic amusement, acknowledging that while we cannot rewrite the laws of physiology, we can certainly script our responses with a wry grin. After all, if life were a perfectly ordered spreadsheet, the occasional hiccup would be downright boring, and the grand comedy of digestive distress would be lost. So let us toast-with a non‑carbonated, low‑acid beverage-to the brief, blazing interludes that keep our medical appointments booked and our mindfulness practices honed. May we learn to navigate the inevitable eruptions with the grace of a seasoned sailor adjusting his sails in a sudden gust. And may we, in moments of calm, reflect on the absurdity of a tiny sphincter deciding the fate of our comfort. All the while remembering that the true victor is the one who, armed with knowledge and a dash of humor, refuses to be out‑witted by a rogue burst of acid. In the grand scheme, the occasional acid flash is just another reminder that our bodies are wonderfully complex, stubborn machines. It nudges us to stay informed, to question the myths that surround digestion, and to seek professional guidance when needed. Moreover, the subtle art of meal timing-a thirty‑minute gap before lying down-can transform a potential flare into a distant memory. Ultimately, the journey from occasional heartburn to chronic GERD is not a linear path, but a winding road filled with dietary experiments, lifestyle tweaks, and occasional setbacks; embracing this road with a blend of curiosity and sarcasm may just be the most therapeutic prescription of all. And remember, a well‑timed antacid can be the punchline that saves the show.
-
Kartikeya Prasad June 13, 2023
Well, look at you, Suman, turning GERD into a philosophical comedy club-who knew stomach acid could be so dramatic? 😏 If we’re handing out medals for the “most creative description of heartburn,” you’d definitely take home gold, silver, and maybe even the bronze for extra flair. That said, the practical takeaway is still crystal clear: avoid those midnight pizza marathons, keep the caffeine monster on a leash, and maybe consider a gentle pillow‑elevating routine before bedtime. And hey, if your reflux ever decides to audition for a starring role, just remember there’s always a doctor on standby with a prescription script that’s less Shakespeare and more science. Keep the sarcasm flowing, but maybe keep the actual acid flowing a little less. 😜
